Monthly Archives: January 2020
Welcome Joe Gilder to the PreSonus Fam!
Please join us in welcoming the esteemed Joe Gilder to the PreSonus family! He has a new Studio One playlist full of tips started… with more episodes to come! Check it out below.
How to Play Faster—By Playing Slower
In the comments for last week’s tip on varipseed-type formant changes, reader Randy Hayes asked if it was possible to change the tempo similarly so that you could play along with something at a slower tempo, then speed it back up (while still being the correct key). This was a common technique with tape, but because pitch and speed were locked together, there would be formant changes—whether you wanted them or not—when you returned the slowed-down track to pitch.
One of the MIDI’s great features is that you can sloooooooow down the tempo, play along with the slowed-down track, then speed it up to make it seem like you have lightning-fast technique. The good news is that with audio, you can slow down Studio One’s tempo without changing pitch, which sounds great in theory. The bad news is that this isn’t always a painless solution, because Events recorded at a slower tempo will likely need to be time-stretched when you return to the original tempo, and you may also need to call up the Inspector for Events or Tracks to specify how the Events should relate to tempo. Also, if there’s a Tempo Track with tempo changes, then you have to offset all the tempo data, as well as make sure you restore it to the proper tempo when you’re done.
Fortunately, there’s an easy way to record along with a song at a slowed-down tempo, and have the correct timing for the recorded part when you restore the song to its original tempo. This complements last week’s formant-changing trick; the technique starts off similarly but ends up quite differently.
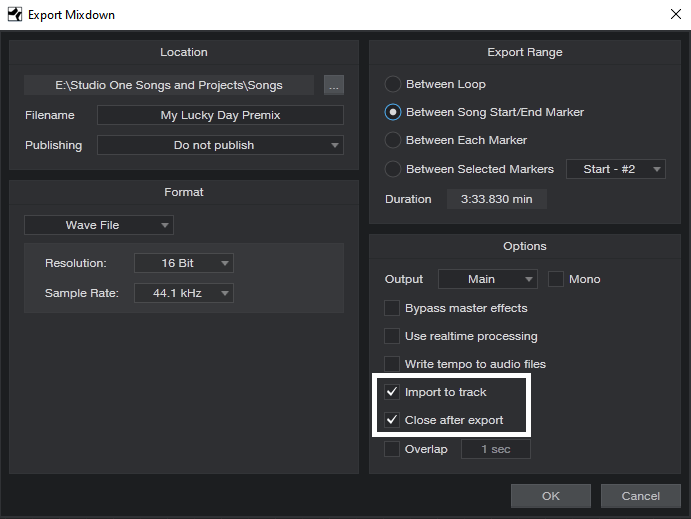
- Create a premix of your existing tracks with the Export Mixdown function. In the dialog box, check Import to Track and Close after Export (Fig. 1; outlined in white).
Figure 1: Use the Export Mixdown function to create a premix.
- After the premix is imported, mute all other tracks except for the Imported premix track.
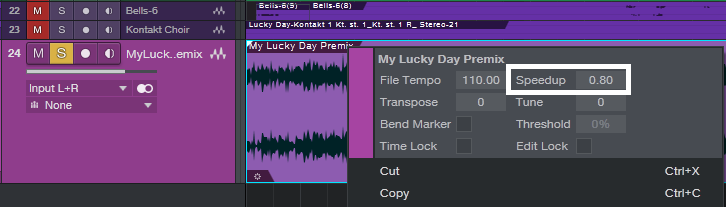
- Select the premixed track, and right-click on it (Fig. 2), or open its Inspector (F4), to access the Speedup parameter. Note that this parameter can also slow down the speed, by entering a value less than 1.00.
Figure 2: Access the Speedup parameter by right-clicking on the premix.
- Slow down the premix to the desired tempo with the Speedup parameter. For example, a Speedup reading of 0.80 means the song’s tempo is 80% as fast as it had been previously. Bear in mind that you can’t do a ridiculous amount of slowing down without affecting the audio quality of the track you’re recording, but overall, Studio One is quite forgiving.
- Record the new track as you listen to the premix’s slowed-down tempo.
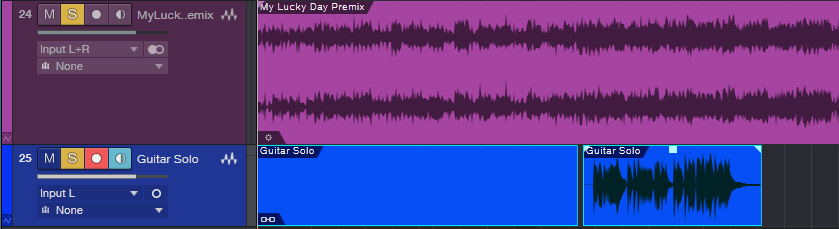
- Before restoring the original tempo, the track you recorded has to start at the song’s beginning. If that’s where you started recording, fine. Otherwise, use the Paint tool to draw an Event between the start of the song and the start of your part, select them both, and type Ctrl+B to merge them together (Fig. 3).
Figure 3: The recorded guitar solo, with an added “dummy” Event that starts at the beginning of the song, prior to merging them together.
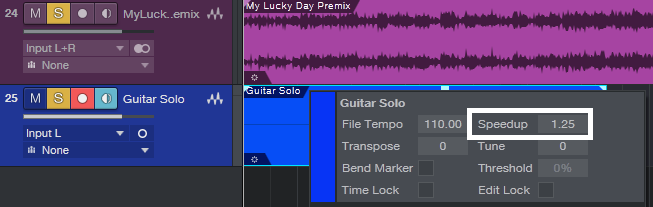
- Now, right-click on the overdub you recorded so you can access its Speedup parameter.
- Open up your calculator to determine how much you need to speed up the overdub. Divide 1 by the slowdown amount to obtain the correct Speedup amount. For example, if you slowed down to 0.80, then 1/0.80 = 1.25. So, set the recorded track’s Speedup parameter to 1.25 (Fig. 4).
Figure 4: Once the newly recorded track goes to the start of the song, change the Speedup parameter to compensate for the slowdown.
- Delete the premix (or mute it if you plan to do more recording at the slower tempo), and unmute the other tracks. The part you recorded should now match the Song’s overall tempo, even if there are tempo changes.
Note that any vibrato will be sped up when you restore the new part to the original tempo. This may be something you want, but if not, just remember to apply a slower vibrato than usual. Also, the timing will be tighter—a note that’s off the beat by a bit will hit closer to the beat when sped up.
Sure, some people might think this is cheating. But back when recording studios started adding EQ or reverb to vocalists, that was considered cheating too. The technique is the skill with which we use our tools, and having “Studio One technique” can be just as important—and valid—as having technique on your chosen instrument.
Just remember, all that matters about music is the emotional impact on the listener. They don’t care what you did to produce that emotional impact!
Varispeed-Type Formant Changes
Back in the days of tape, when dinosaurs ruled the earth and gas station attendants checked your oil, variable-speed tape recorders allowed changing the pitch of all the tracks with a single control. This was useful for many applications. The most common were speeding up masters a bit to make them a little brighter and tighter, doing tape flanging, and perhaps the most popular, changing vocal formants. If you transposed the recorder’s pitch down a little bit, recorded a vocal as you sang along with the lower pitch, and then transposed back up again on playback, the vocal formant would be higher and brighter. Similarly, for a darker, warmer sound, you could transpose up, sing along with that, and transpose back down again. The same principle worked with other instruments, but vocals were the most popular candidates for this technique.
The main limitation (although it could also be an advantage in some situations) is that the tempo and pitch were interdependent—a higher pitch meant a faster speed, and a lower pitch, a slower speed. This was useful for masters, because you could speed up and brighten a track by upping the speed by 2% or so. The Friday tip for June 8, 2018 covered how to emulate true, variable speed tape effects when working on a final stereo mix.
A major advantage of today’s digital audio technology is that pitch and tempo can be independent, and one of Studio One’s attributes is that the audio engine retains its sound quality with reasonable pitch changes (e.g., a few semitones). This makes it very easy to do the old tape trick of changing vocal formants; here’s how.
- First, create a premix of your existing tracks with the Export Mixdown function. In the dialog box, check Import to Track and Close after Export (Fig. 1).
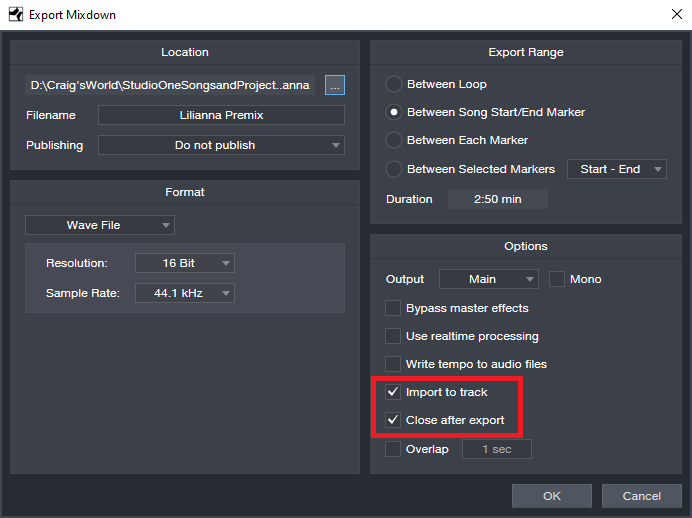
Figure 1: Use the Export Mixdown function to create a premix.
- After the premix is imported, mute all other tracks except for the Imported premix track.
- Select the premixed track, and right-click on it (Fig. 2), or open its Inspector (F4), to access the Transpose and Tune parameters.
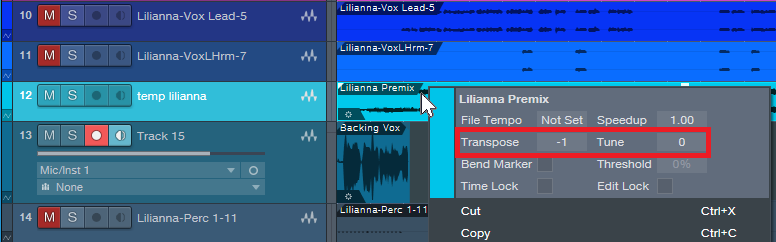
Figure 2: You can access the Transpose and Tune parameters by right-clicking on the premix.
- To brighten the vocal formant, use the Tune and/or Transpose function to lower the pitch.
- Record the vocal track as you listen to the premix.
- After recording the vocal track, right-click on the vocal Event, or open its Inspector, and tune it up by as much as you tuned the premix track down. For example, if you tuned the premix down a semitone, tune the vocal track up a semitone.
- Delete the premix (or mute it if you plan to do more formant-shifted tracks), unmute the other tracks, and enjoy your formant-shifted vocal.
This is especially useful when doubling parts, because the double can have a slightly different timbre. And with background vocals, shift some formants up, and some formants down, for a bigger, more interesting sound. And of course, if you just can’t quite hit that high note…you’re covered. I promise I won’t tell.
I also like using this with guitar and other instruments. I’ve gotten away with pitching guitar up 7 semitones for a bright sound that splits the difference between a standard guitar sound, and one that’s more like “Nashville” tuning (as described in the Friday Tip for December 1, 2019). At the other end of the tonal spectrum, playing along with the premix tuned up, and pitching back down, is like using a low tuning on a guitar—great for those massive metal guitar sounds.
—————————————
As we enter 2020, thank you very much for your support of these blog posts, and your comments. Also, thank you for supporting the Studio One book series that I’m writing. When I wrote the first book, I wondered if there would be any demand for it, or whether I was just wasting my time. Well, you’ve answered that question… so now I’m working on book #5 of the series, about how to record great guitar sounds with Studio One. It won’t be done for a while, but it wouldn’t have been done at all without your support (or the great-sounding new amp sims, for that matter).
Finally, let’s all thank Ryan Roullard and Chad Schoonmaker, who wrangle the blog and social media each week to get this blog posted and promoted. It’s not like they don’t already have enough to do at PreSonus, which makes their involvement just that much more appreciated. Thanks guys!